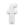A Few Recent Loggerhead Shrikes
There’s always a few Loggerhead Shrikes that winter-over on Antelope Island and I find them to be fascinating subjects. Their approachability is very unpredictable but occasionally they’ll allow me to get close, especially when it’s very cold in the mornings or if they’re about to hack up a pellet. These are images I was able to get in the last few weeks. ***Note: The last image in this post is graphic. If your sensibilities might be offended by such a photo please stop scrolling before you get to the last (6th) image. 1/3200, f/5.6, ISO 500, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc This bird was practicing its springtime melodic repertoire a few weeks early (image taken on 2/5/12). It was a relatively warm, sunny morning and it was singing its little heart out (if you can call shrike calls “singing”). 1/2000, f/6.3, ISO 400, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc With their black masks these shrikes always remind me of little bandits and they have an attitude to go along with that perception. They get their name from their unusually large head (loggerhead means “block head”). 1/8000, f/5.6, ISO 500, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc I like the soft, even light and the setting in this image even though the twigs in front of the bird may not be ideal for some. 1/640, f/7.1, ISO 640, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc I’m including this shot just for fun. I liked the fluffy, relaxed pose to go along with the yawn. 1/1250, f/7.1, ISO 500, 500…