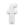Agonistic (fighting) Behavior in Male Short-eared Owls
I recently returned from one of my favorite places in the world – Red Rock Lakes National Wildlife Refuge. Last year I was able to photograph nesting Short-eared Owls carrying voles to their young but this year, because of the very cold spring, nesting hadn’t even begun. Instead the owls were competing for territory and mates and pairing up. On one morning I was incredibly lucky to find two males trying to impress a female with their aerial prowess and fighting skills. They were so engrossed in their activities that they pretty much ignored me. Canon 7D, 1/2000, f/7.1, ISO 500, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc Often one male would be on the ground when the other male would swoop in on him. Here the foreground bird has just lifted off to meet his adversary. Canon 7D, 1/2000, f/7.1, ISO 500, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc As was often the case the birds didn’t make actual contact. In researching this behavior I’ve learned that they will sometimes lock talons and fall to the ground before releasing. I suspect that as they rush toward each other they look for a weakness in defense – if they spot one in the other birds defensive body position they would likely make aggressive contact. Canon 7D, 1/2000, f/7.1, ISO 500, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc Most of the time both birds stayed on the ground or flew very low but occasionally one of the owls would fly several hundred feet up and circle over the other male (and the female, who was…