Tag: great salt lake institute
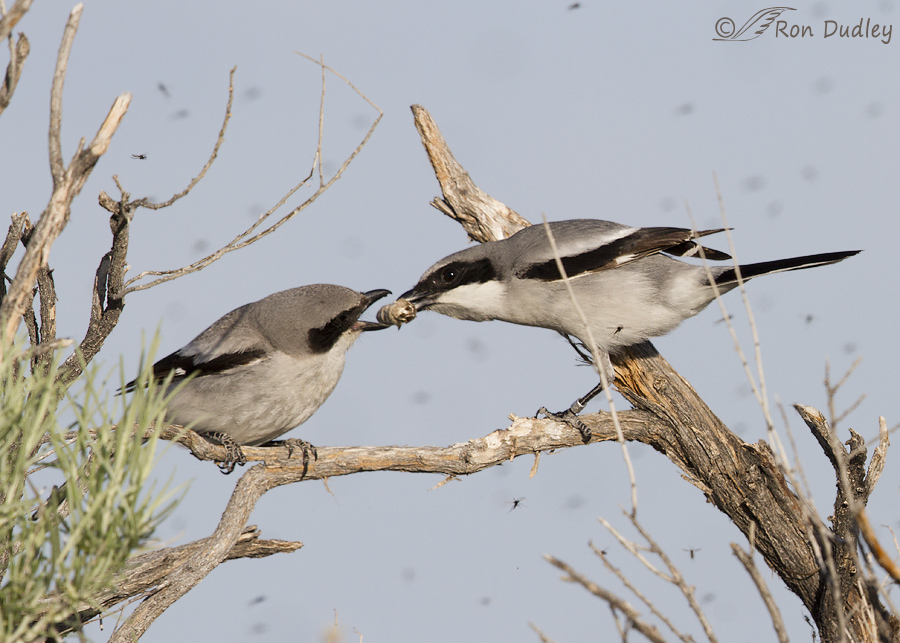
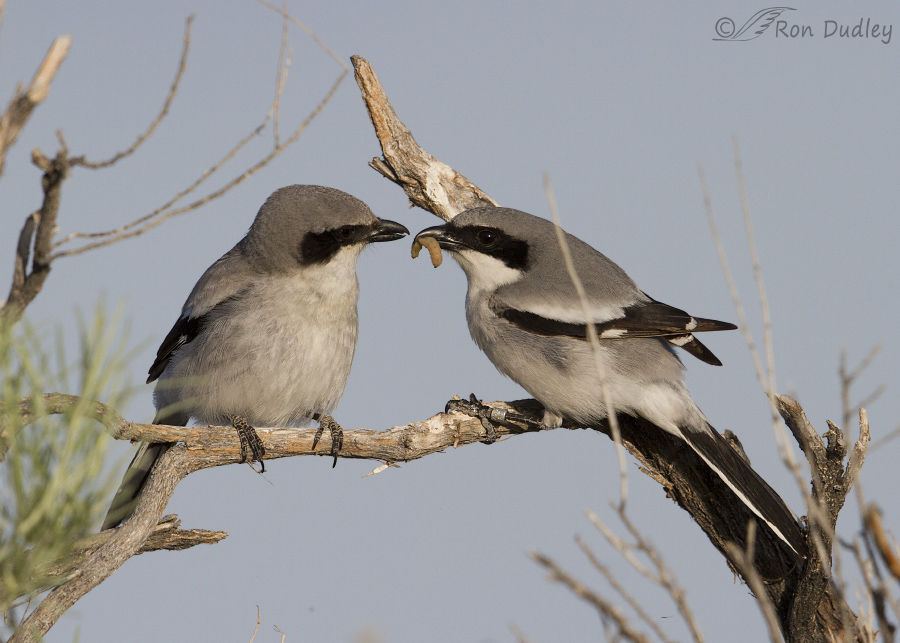
Loggerhead Shrikes “Courtship Feeding”
Yesterday My Blog Followers Gave Me A Case Of The Warm Fuzzies
Jaimi Butler, Badass
Loggerhead Shrikes On Antelope Island – Then And Now
Loggerhead Shrikes, Spiders And Great Salt Lake Institute
Male Loggerhead Shrike Feeding His Mate
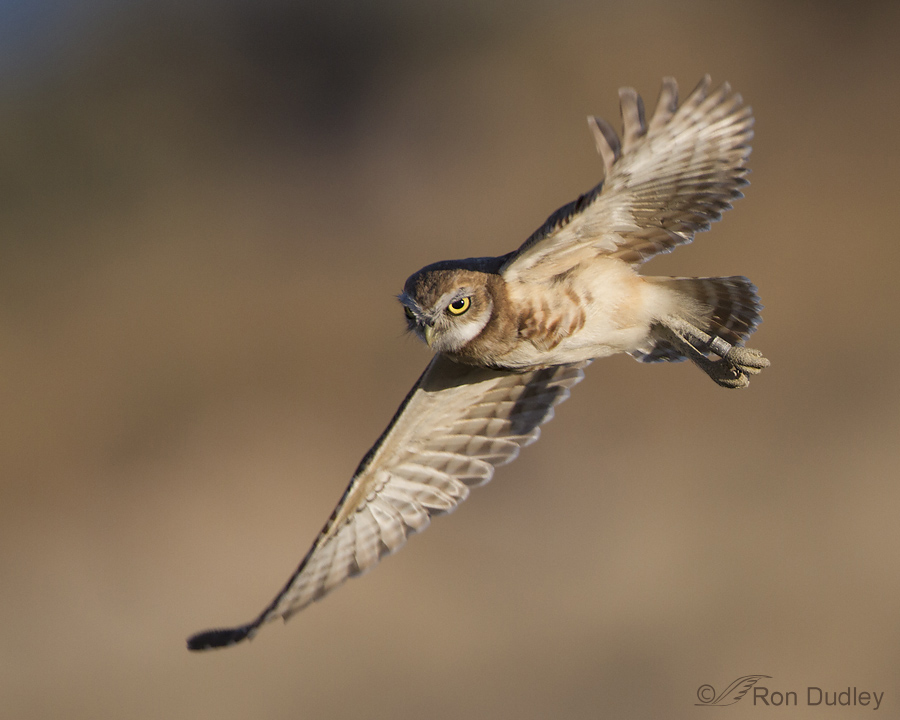
Burrowing Owls And Banding
Enveloped By Shrikes!
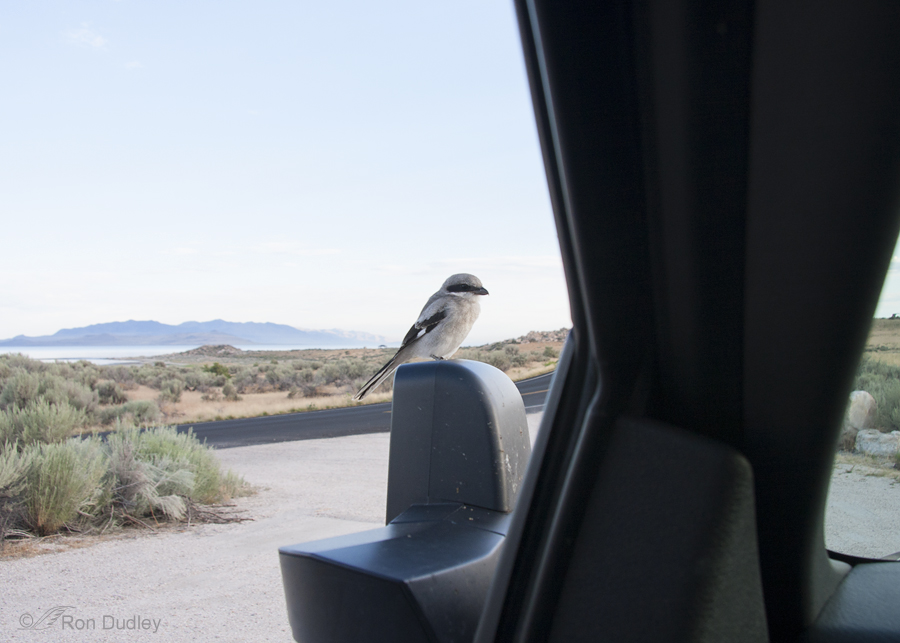
Juvenile Loggerhead Shrike Take-off
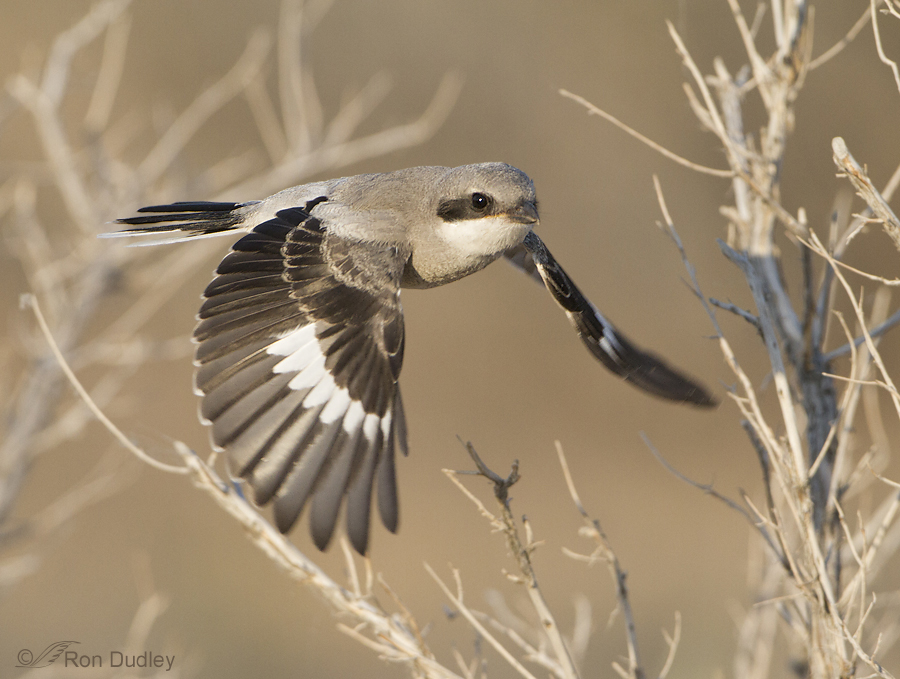

Many of the young Loggerhead Shrikes on Antelope Island have now fledged and are learning the ropes. They’re ornery, fun, fierce and fearless. Twice I’ve had one almost fly into my open pickup window, another one very nearly landed on my lens hood sticking out a window and yet another landed on the pickup itself.
Birds, Spiders, Brine Flies and Mercury Contamination on Antelope Island
Last Sunday I found this Northern Shrike on Antelope Island enthusiastically singing away as if spring were already in full bloom. Their predatory habits and interesting behaviors make them a favorite species for me but when I got home that day I read an article in the Salt Lake Tribune that made me wonder just how healthy their populations near the Great Salt Lake really are. North end of Antelope Island, 2/5/12 The reason for my concern is a bit complex but I’ll summarize: For over 100 years smelting operations have been responsible for high levels of elemental mercury in the Great Salt Lake and its sediments. Microorganisms in the lake convert the mercury to methyl mercury which is the toxic form of the element that can be absorbed by tissues of living things. Brine fly larvae living in the lake then absorb the methyl mercury and when they hatch the adult flies are consumed by spiders living in the vegetation around the lake. Finally, those spiders are eaten by the many bird species living and nesting along the shoreline. But very little is known about the movement of mercury compounds through Great Salt Lake ecosystems, including the possible effects of toxic methyl mercury on birds so Westminster College’s Great Salt Lake Institute was recently awarded a $250,000 grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation to study its possible effects. Antelope Island causeway, 8/29/11 The number and total biomass of brine flies in late summer around the lake literally boggles the mind but this shot should give you some idea. It was taken in late August of…
Loggerhead Shrikes “Courtship Feeding”
Yesterday My Blog Followers Gave Me A Case Of The Warm Fuzzies
Jaimi Butler, Badass
Loggerhead Shrikes On Antelope Island – Then And Now
Loggerhead Shrikes, Spiders And Great Salt Lake Institute
Male Loggerhead Shrike Feeding His Mate
Burrowing Owls And Banding
Enveloped By Shrikes!
Juvenile Loggerhead Shrike Take-off

Many of the young Loggerhead Shrikes on Antelope Island have now fledged and are learning the ropes. They’re ornery, fun, fierce and fearless. Twice I’ve had one almost fly into my open pickup window, another one very nearly landed on my lens hood sticking out a window and yet another landed on the pickup itself.
Birds, Spiders, Brine Flies and Mercury Contamination on Antelope Island
Last Sunday I found this Northern Shrike on Antelope Island enthusiastically singing away as if spring were already in full bloom. Their predatory habits and interesting behaviors make them a favorite species for me but when I got home that day I read an article in the Salt Lake Tribune that made me wonder just how healthy their populations near the Great Salt Lake really are. North end of Antelope Island, 2/5/12 The reason for my concern is a bit complex but I’ll summarize: For over 100 years smelting operations have been responsible for high levels of elemental mercury in the Great Salt Lake and its sediments. Microorganisms in the lake convert the mercury to methyl mercury which is the toxic form of the element that can be absorbed by tissues of living things. Brine fly larvae living in the lake then absorb the methyl mercury and when they hatch the adult flies are consumed by spiders living in the vegetation around the lake. Finally, those spiders are eaten by the many bird species living and nesting along the shoreline. But very little is known about the movement of mercury compounds through Great Salt Lake ecosystems, including the possible effects of toxic methyl mercury on birds so Westminster College’s Great Salt Lake Institute was recently awarded a $250,000 grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation to study its possible effects. Antelope Island causeway, 8/29/11 The number and total biomass of brine flies in late summer around the lake literally boggles the mind but this shot should give you some idea. It was taken in late August of…